Technology has extended many kinds of human capacity, and the sensor has extended the range of human perception. With the rapid development of modern technology. There is a heavy demand for IoT, big data, cloud computing technology and so on. It is widely applied to economics, the national defense science and technology, the people's livelihood and any other areas.
Understanding Sensors and Their Purpose
It's a jungle out there with countless sensor types. From humble temperature sensors to sophisticated LiDAR systems, they all have unique roles in our tech-driven world. So, the first step to choosing the right sensor is understanding what they do.
Sensors are the eyes and ears of our devices, providing valuable data from the physical world. They monitor environmental factors, detect changes, and relay this info to other parts of the system. What sensor you choose depends largely on what you want to measure.
Types of Sensors
The variety of sensors can make your head spin! Here's a snapshot of some of the most common ones:
1. Temperature Sensors: As the name suggests, these track temperature variations. They're the bread and butter of HVAC systems and many industrial processes.
2. Proximity Sensors: Handy for robotics and security systems, these sensors detect the presence or absence of an object within a certain range.
3. Pressure Sensors: Monitoring air or fluid pressure is their forte. You'll find them in vehicles, medical devices, and weather monitoring systems.
4. Light Sensors: These detect light levels and are commonly used in automatic lighting systems and cameras.
So for normally, And the sensors are divided into the wireless sensor and conventional wired sensor.
Conventional wired sensors connect the device that receives input, has the advantage of high accuracy, durable and can be used many times without replacement.
The wireless sensor is a wireless data communication collector that integrates the functions of data acquisition, data management and data communication, has the advantage of low-power operation, wireless data transport, no wiring, flexible installation and debugging and so on.
The communication protocols are divided into wireless communication protocols and wired communication protocols. The communication protocol defines the format used by the data unit, the information and meaning that the information unit should contain, the connection mode, and the timing when the information is sent and received, to ensure the smooth transfer of data to the determined place.
The types of communication protocols have RFID, infrared, ZigBee, Bluetooth, GPRS,4G, Wifi and NB-IoT. The communication protocols have MBus, USB, RS232, RS485 and ethernet.
Some Details of Each Protocols as Following :
A: Wireless Protocols
Wireless communication has become a crucial part of modern technology. From remote control toys to advanced industrial machinery, wireless protocols play a critical role. Here are some common ones:
1. RFID (Radio Frequency Identification): RFID is used for contactless data exchange, most commonly in access control and asset tracking systems.
2. Infrared: Infrared communication is used in short-range applications, such as television remotes and short-range data transfer between devices.
3. ZigBee: ZigBee is a low-power, low-data-rate wireless network mainly used in industrial settings, smart homes, and remote control systems.
4. Bluetooth: You probably know this one! Bluetooth is used for short-range, point-to-point, and point-to-multipoint communication. It's perfect for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, and headphones.
5. GPRS (General Packet Radio Service): GPRS is used in mobile communication for internet access, multimedia messaging, and location-based services.
6. 4G: The fourth generation of cellular technology, 4G provides mobile ultra-broadband internet access for mobile phones, laptops, and other mobile devices.
7. Wifi: Wifi is a wireless networking protocol that allows devices to communicate without direct cable connections. It's extensively used in home networks, office networks, and public hotspots.
8. NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things): NB-IoT is a low-power wide-area network protocol designed to connect devices across long distances in hard-to-reach areas. It's ideal for IoT applications.
B: Wired Protocols
Even in our wireless world, wired protocols still have a crucial role, particularly in industrial and high-data-rate applications.
1. MBus (Meter-Bus): MBus is a European standard for remote reading of heat meters and other consumption meters.
2. USB (Universal Serial Bus): USB is used for connection, communication, and power supply between computers and their peripheral devices.
3. RS232: This is a standard for serial communication transmission of data. It's traditionally used in computer serial ports.
4. RS485: Similar to RS232, RS485 supports more nodes per network and longer cable lengths. It's used in industrial control systems and building automation.
5. Ethernet: Ethernet is widely used in local area networks (LANs). It provides high speed and reliable communication between devices.
Selecting the appropriate protocol will largely depend on the application and the environment. Always consider factors like range, power consumption, data rate, and the type of devices being connected when making your choice.
In 1983, based on the RS-422 Industrial Bus standard, the Electronic Industry Association formulated and issued the RS-485 industrial Bus standard. The RS-485 bus-standard specifies standards for the electrical properties of bus interfaces that are defined for the two logical states: The positive level is between +2V ~ +6V, indicating a logical state; A negative level between -2V and -6V indicates another logical state. Digital signal adopts differential transmission mode, which can effectively reduce the interference of noise signal.
It can effectively support multiple sub-nodes, communication distance and high sensitivity of information receiving. In industrial communication network, RS - 485 bus is mainly used in general and external information transmission and data exchange, all kinds of industrial equipment with effective for noise suppression capability, efficient data transfer rate and good reliability of data transmission and scalable communication cable length is unmatched by other many industrial communication standards.Therefore, the RS-485 has been widely used in many fields.
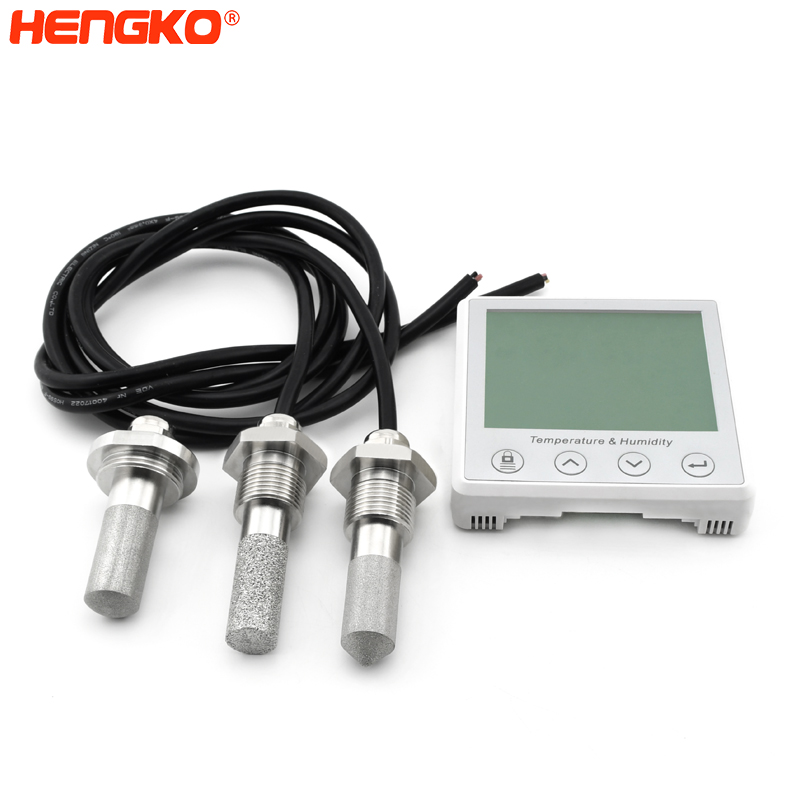
Communication protocol of the HENGKO temperature and humidity sensor and gas sensor is RS-485. In the temperature and humidity and gas detector, RS-485 bus can transmit information and exchange data directly with the sensor to ensure the data Immediate response and accuracy.
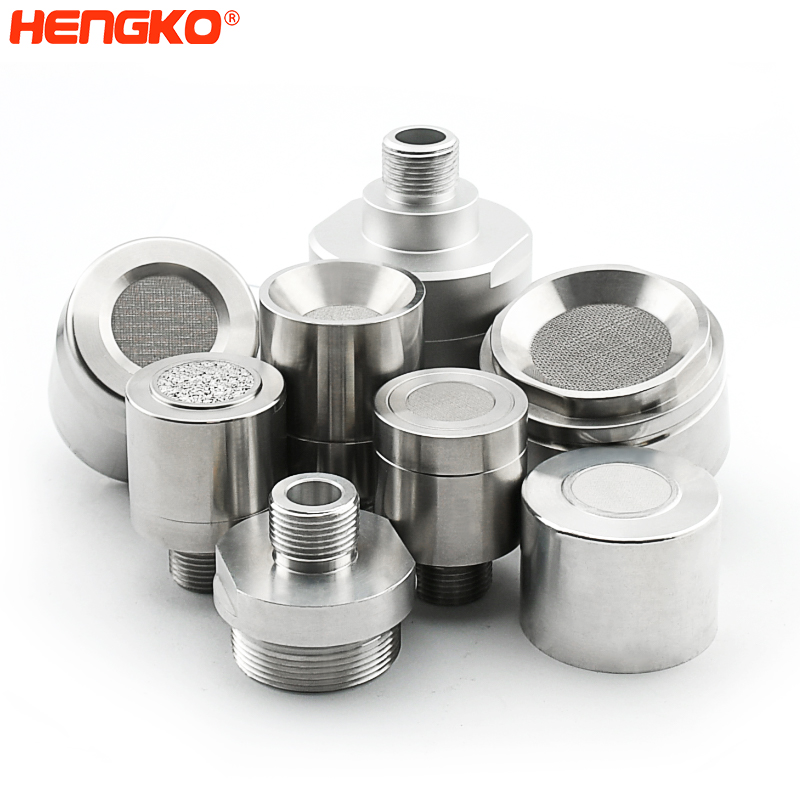
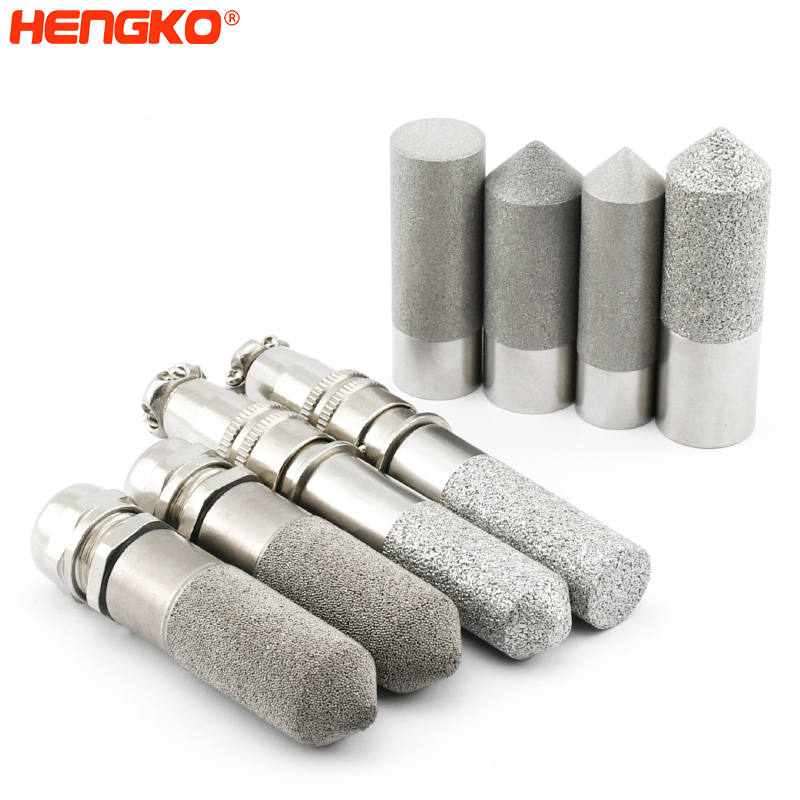
Besides, the gas sensor probe as a measuring element has a great effect on the sensor measuring accuracy. According to the different measuring environment of the sensor, it is very important to choose the probe housing. Such as the stainless steel probe housing has the advantage of high-temperature resistance, anti-corrosion, waterproof, dust removal, is available for high temperature and humidity, large dust and other severe environments.
With the constant development of technology, the requirement of the various sensor has more and more high.
HENGKO has more than 10 years of OEM/ODM customized experience and professional co-design
and aided design capacity. We have a professional design team the provides technical assistance.
We will provide you excellent temperature and humidity sensor/ transmitter/probe, gas sensor/alarm/module/element and so on.
Post time: Oct-31-2020