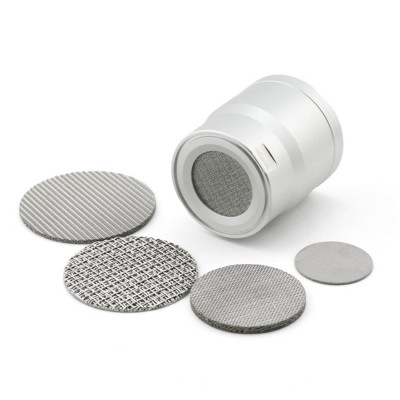
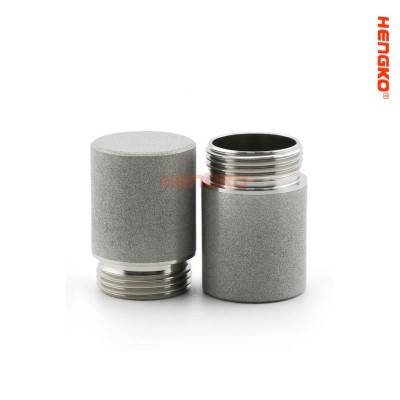
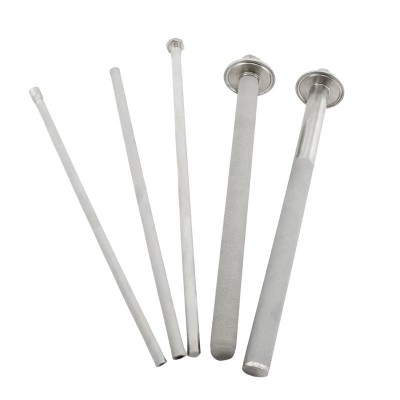
Porous Metal Meaning
What is Porous Metal
In Short, Porous metals are materials that have a three-dimensional interconnected network of pores, or voids, in their microstructure that allow fluids or gases to flow through the material.
These pores range in size from nanometers to millimeters and are usually formed by processes such as sintering, foaming or electroplating. Porous metals have unique properties that make them useful in a variety of applications, including filtration, catalysis, energy storage, and biomedical engineering.
The porosity of these metals can be controlled and tailored to meet specific requirements, such as pore size, pore volume, and surface area. This tunability allows tailoring porous metals to meet the needs of different applications. Furthermore, the interconnected pore structure of porous metals allows high permeability and low pressure drop, which facilitates fluid flow and mass transfer processes.
Nowadays, Porous metals are usually made from common engineering metals such as aluminum, titanium, nickel and copper, but can also be made from less common materials such as magnesium or zinc. The properties of porous metals depend on the type of metal used, the manufacturing process, and the size and distribution of pores. Porous metals can be made in various forms such as sheets, tubes, foams and powders, making them versatile materials for a variety of applications.
As follow is popular list of porous metals structure diagram in the market, hope it will make you know clear for the porous metal.

The Corrosion-Resistant Solution for Advanced Filtration and Gas Diffusion Applications
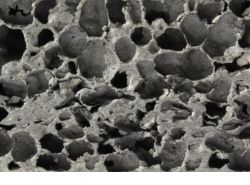
Porous Aluminum
Lightweight and Versatile for Improved Heat Transfer and Acoustic Attenuation

Porous Nickel
High-Strength, High-Temperature Resistance, Ideal for Advanced Catalysis and Battery Applications.

The Cost-Effective Solution for Precision Sintering and Controlled Porosity in Bearings and Filters.
Main Features & Advantage
Porosity:
As the name suggests, porous metals are characterized by their network of interconnected pores. Porosity can vary depending on the manufacturing process and range from a few percent to over 90%.
Surface Area:
Porous metals have a high surface area to volume ratio due to their porous structure. This increased surface area could be used in applications such as catalysis, filtration and energy storage.
Mechanical properties:
Porous metals exhibit a range of mechanical properties, depending on the material and porosity. The mechanical properties of metals can be tailored by tuning pore size, shape and distribution.
Biocompatibility:
Certain porous metals, such as titanium and its alloys, are biocompatible and can be used in biomedical applications such as implants.
Fluid flow:
The interconnected pores in porous metals allow fluid flow, making them useful in applications such as filtration and separation.
Thermal and electrical conductivity:
The thermal and electrical conductivity of porous metals can be tuned by varying the porosity and metal used in the fabrication process.
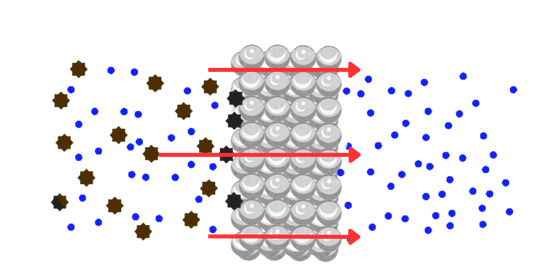
High-Performance Filters with Controlled Pore Sizes and Optimal Flow Rates for Gas and Liquid Applications.
Durable and Wear-Resistant Components for Bearings and Hydraulic Systems with Enhanced Lubrication Properties.
Tailored Solutions for Enhanced Heat and Mass Transfer in Chemical and Petrochemical Processes with High Structural Integrity.
Best Solution for Design & Engineering of High Requires Filtration Problem
Above preliminary understanding, We Know Sintered porous metal can offer various customizable flow and filtration properties. And This unique material is produced through sintering, which involves heating metal powder to a temperature just below its melting point, allowing the particles to fuse while maintaining the desired porosity. You can easily shape it, machine it, and regulate its porosity, making it a versatile material for developing any number of unique products or system solutions that involve regulating and controlling liquids and gases.
Suppose you Also Looking for Some Special Materials for Your Filtration System. In that case, We invite you to contact us today to explore how our porous metal media solutions can assist in resolving your design engineering challenges. Let's collaborate and identify tailored solutions that meet your unique requirements.
Typical Application for Porous Metal
Porous metals and porous metal filters are used in a wide range of applications due to their special properties,
including high permeability, controlled porosity, and mechanical strength. Below are some typical applications:
1. Filtration and Separation:
Porous metal filters are widely used in industrial filtration systems, where they help separate solids from liquids or gases.
They are particularly useful in industries such as petrochemical, chemical processing, and oil and gas due to their resistance to high temperatures and corrosive materials.
2. Sparging and Diffusion:
In sparging, a porous metal is used to diffuse a gas into a liquid, often to aerate the liquid.
This is commonly used in wastewater treatment, pharmaceutical production, and food and beverage processes.
3. Pressure Regulation:
Porous metal parts can be used in pressure regulation devices like pressure relief valves or breathers in various industries including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
4. Sensors:
Porous metals can be used in certain types of sensors due to their ability to allow gases and liquids to pass through.
These can be found in environmental monitoring, industrial processing, and healthcare applications.
5. Sound Damping:
Porous metals are often used for sound damping or noise reduction in various industries, from automotive exhaust systems to industrial machinery.
6. Heat Exchangers:
Porous metals offer good thermal conductivity and heat transfer characteristics, making them excellent for heat exchanger applications, especially in industries that work with high temperatures.
7. Catalyst Supports:
In chemical processes, porous metal can be used as a catalyst support, allowing for a larger surface area for the reaction to occur. This is commonly seen in the petrochemical industry.
8. Battery Electrodes:
Porous metals can be used in the production of battery electrodes. The porosity allows for more surface area, enhancing the battery's efficiency.
9. Biomedical Applications:
Porous metals, especially porous titanium and its alloys, have found extensive applications in the biomedical field, such as in orthopedic implants and dental implants. Their porous nature promotes bone ingrowth, leading to better integration with the body.
10. Fuel Cells:
Porous metal components can serve as electrodes in fuel cells, allowing gases to easily move through while conducting electricity.
Please note that the specifics of application of porous metal or filters depend on the type of porous metal or alloy and the exact nature of the porosity (size, distribution, and connectivity of the pores).
so if have any questions for application of porous sintered metal filter, please feel free to contact HENGKO by email ka@hengko.com.
FAQ About Porous Metal
1. Why use porous metal to make filter ?
Porous metal is a material with a unique structure that contains interconnected pores or voids within its solid framework. The pore size and distribution can be tailored to meet specific application requirements, making it a versatile material for a range of industries.
So as those special function, Porous metals are commonly used in the fabrication of filters due to several reasons:
1. Controlled Pore Size: Porous metals can be engineered to have very precise pore sizes. This allows for the creation of filters with specific filtering capabilities, such as removing particles of a certain size.
2. High Strength: Metal filters have high mechanical strength, which makes them robust and durable. They can withstand high pressure and temperature conditions that might damage other types of filters.
3. Chemical Resistance: Metals are often resistant to a variety of chemicals, making them suitable for use in environments where they might be exposed to corrosive substances.
4. Reusability: Metal filters can be cleaned and reused, which is both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
5. Thermal Stability: Metallic filters can sustain in high-temperature applications, which might not be the case with filters made from polymer materials.
6. Permeability: Due to their porous nature, these materials permit a high degree of fluid flow while efficiently capturing and retaining particles.
7. Backwash Capability: Metal filters can be backwashed to remove trapped particles, which allows for the recovery of valuable materials and prolongs the lifespan of the filter.
Hence, depending upon the application and the type of fluid that needs to be filtered, porous metal filters can be an excellent choice.
2. How is porous metal made?
Porous metal is typically produced through a process called sintering, which involves heating metal powder to a temperature just below its melting point, allowing the particles to fuse together while maintaining the desired porosity.
The process of making porous metals involves creating voids or pores within the metal. There are several methods used to achieve this, including powder metallurgy, sintering, and additive manufacturing. Below is a simplified description of a common method, powder metallurgy:
1. Metal Powder Production: The first step in creating porous metal is to produce metal powder. This can be done in several ways, including atomization (spraying a stream of molten metal into a chamber where it solidifies into powder) or mechanical milling.
2. Mixing and Compacting: The metal powder is mixed with a binding agent or space holder material to help maintain the structure during processing. The mixture is then compacted under high pressure in a die to form a "green" compact. The shape of the die will determine the final shape of the porous metal part.
3. Sintering: The green compact is then heated in a furnace to a temperature below the melting point of the metal. This process, known as sintering, causes the metal particles to bond together. The high temperature also causes the binder or space holder material to burn off or evaporate, leaving behind pores.
4. Cooling and Finishing: After sintering, the metal part is allowed to cool, then it may undergo additional processes like finishing or coating to improve its surface characteristics.
An alternative approach is using additive manufacturing (commonly known as 3D printing), where a metal powder is selectively melted layer by layer based on a digital model. This can create complex shapes and internal pore structures that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
The pore size, distribution, and connectivity can be controlled to a large extent during the manufacturing process, which makes porous metals suitable for a wide range of applications, including filtration.
3. What are the advantages of porous metals?
The advantages of porous metals include high surface area-to-volume ratio, mechanical strength, thermal and electrical conductivity, and the ability to tailor pore size and distribution. These properties make it useful in applications such as catalysis, filtration, and energy storage.
4. What are the limitations of porous metals?
Porous metals may have lower bulk strength compared to non-porous metals due to the presence of voids within the material. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly.
5. What is the difference between open-cell and closed-cell porous metals?
Open-cell porous metals have interconnected pores that are accessible from the surface of the material, while closed-cell porous metals have sealed pores that are not accessible from the surface.
6. What types of metals can be used to make porous metals?
Porous metals can be made from a range of metals, including aluminum, titanium, nickel, copper, and stainless steel, among others.
7. What are the applications of porous metals?
Porous metals have applications in industries such as aerospace, biomedical engineering, chemical processing, and energy storage, among others.
8. What are the challenges associated with manufacturing porous metals?
The challenges associated with manufacturing porous metals include maintaining the desired porosity, ensuring good mechanical properties, and controlling the pore size and distribution.
9. What is the porosity of porous metals?
The porosity of porous metals can range from a few percent up to 90% or higher, depending on the application requirements.
10. What is the significance of pore size and distribution in porous metals?
The pore size and distribution in porous metals are critical to determining the material's properties, such as permeability, mechanical strength, and surface area. This is because pore size affects how easily fluids can flow through the material and how much surface area is available for reactions to occur.
11. Can porous metals be customized for specific applications?
Yes, porous metals can be customized for specific applications by adjusting the pore size and distribution, as well as the type of metal used.
12. What is the lifespan of porous metals?
The lifespan of porous metals depends on the application and the specific material used. Generally, porous metals have a long lifespan due to their high durability and resistance to corrosion.
13. Can porous metals be recycled?
Yes, porous metals can be recycled by melting the material down and reusing it in new applications.
14. Are porous metals safe for use in biomedical applications?
Certain types of porous metals, such as titanium and tantalum, are biocompatible and can be used safely in biomedical applications. The porous structure can encourage bone growth and improve integration with surrounding tissue.
15. How can porous metals be tested for their properties?
Porous metals can be tested for properties such as porosity, permeability, and mechanical strength using techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM), gas permeability tests, and compression tests.
Discover the endless possibilities of porous metals! From improved heat transfer to enhanced filtration, porous metals offer unique benefits that can revolutionize your industry. Contact us today to learn more and start exploring the power of porous metals.
Everything you need to contact HENGKO get Solution
Send your message to us: