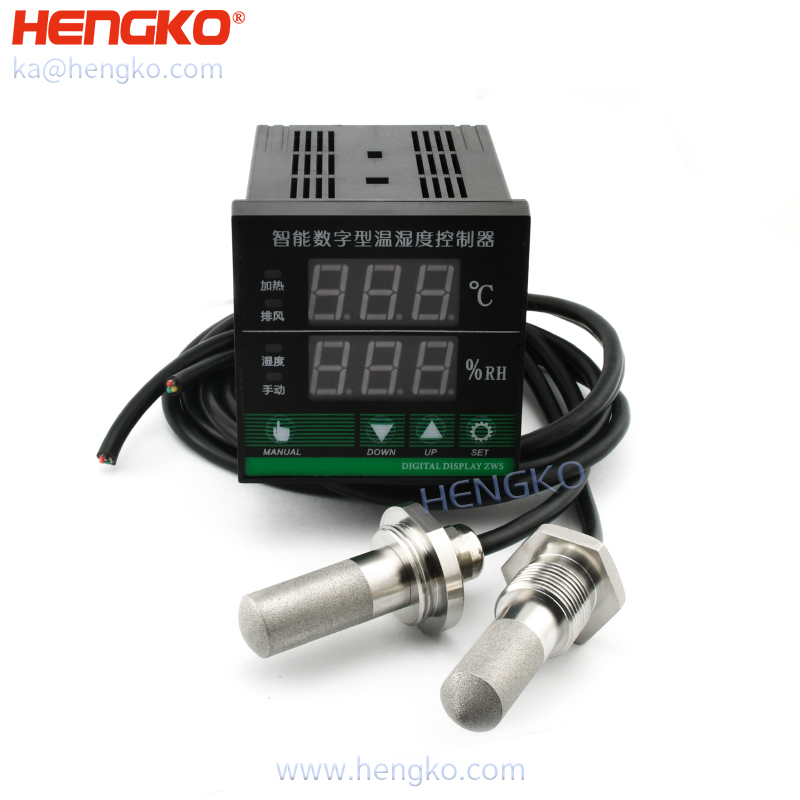
Ever wondered how your home thermostat maintains that comfy room temperature? Or how weather forecasts can predict humidity levels? Temperature and humidity sensors, tiny but powerful gadgets, make it all possible. But what are these sensors, and how do they function?
How Does Temperature and Humidity Sensor Work
As We Know, Temperature and humidity sensors, also known as hygrometers, are devices used to measure and monitor environmental conditions.
They work based on specific physical principles to detect and quantify temperature and humidity levels. Let's explore how each of them works:
1. Temperature Sensor:
Temperature sensors measure the degree of hotness or coldness of an object or the surrounding environment. There are several types of temperature sensors, but one common type is the thermocouple. Thermocouples consist of two different metal wires joined at one end, forming a junction. When this junction is exposed to a temperature gradient, a voltage difference is generated between the two wires due to the Seebeck effect.
The Seebeck effect is a phenomenon where a temperature difference between two dissimilar conductors creates an electric potential. This voltage difference is then correlated to the temperature using a known relationship between voltage and temperature. Modern temperature sensors, like digital thermocouples or resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), convert this voltage into a digital signal that can be read and interpreted by microcontrollers or other electronic devices.
2. Humidity Sensor:
Humidity sensors measure the amount of moisture or water vapor present in the air, commonly expressed as a percentage relative to the maximum amount of water vapor the air can hold at a given temperature (relative humidity).
There are various types of humidity sensors, including capacitive, resistive, and thermal conductivity-based sensors.
A: Capacitive humidity sensors work by measuring the capacitance changes of a dielectric material in response to the absorption or desorption of water molecules. As humidity increases, the dielectric material absorbs water vapor, leading to a change in capacitance, which is then converted into a humidity value.
B: Resistive humidity sensors use a moisture-absorbing material with variable electrical resistance. When the material absorbs moisture, its resistance changes, and this variation in resistance is used to determine the humidity level.
C: Thermal conductivity-based humidity sensors consist of a heated element and a temperature sensor. As moisture content in the air changes, the heat transfer characteristics of the surrounding air change as well. By measuring the change in temperature or power needed to maintain a constant temperature, the humidity level can be calculated.
In summary, temperature and humidity sensors rely on different physical principles to measure these environmental parameters. Temperature sensors exploit the Seebeck effect in thermocouples or resistance changes in RTDs to measure temperature, while humidity sensors use capacitance, resistance, or thermal conductivity changes to detect the presence of water vapor and determine humidity levels. These sensors play crucial roles in various applications, from weather monitoring and climate control to industrial processes and electronic devices.
Common Types of Temperature Sensors
There are several kinds of temperature sensors, but let's focus on the most common ones.
1. Thermocouples
These are a type of sensor that measure temperature using the Seebeck effect, where differing metals generate a voltage proportional to temperature. Simple, inexpensive, and versatile, they can measure a broad range of temperatures.
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
RTDs utilize the principle that the resistance of a metal wire increases with temperature. They are accurate, stable, and can measure a wide temperature range, making them ideal for industrial applications.
2. Thermistors
Thermistors, or thermal resistors, work on the same principle as RTDs but are made from ceramic or polymer materials. They are highly accurate for a limited temperature range, making them excellent for specific, controlled environments.
Common Types of Humidity Sensors
Let's explore the three main types of humidity sensors.
3. Capacitive Humidity Sensors
These sensors measure humidity by assessing the change in capacitance of a thin polymer film. They are commonly used due to their high accuracy, stability, and durability.
Resistive Humidity Sensors
These sensors detect humidity through the change in resistance of an organic or inorganic material. They are less expensive than capacitive sensors, but also less precise.
Thermal Conductivity Humidity Sensors
These sensors gauge humidity by measuring the change in thermal conductivity of air as humidity changes. Though less common, they are highly beneficial for measuring high levels of humidity.
Classify by Connection Way
Temperature and humidity sensor is ubiquitous in our life. For instance, greenhouse, warehouse, subway and other environments that need humidity and temperature to monitor the humidity and temperature situation. They have various application area, do you know the common type of them?
1. Analog temperature and humidity sensor
Integrated temperature and humidity sensor adopt a digital integrated sensor as a probe with a digital processing circuit that can transform the temperature and relative humidity sensor of the environment the corresponding standard analog signal(4-20mA、0-5V or 0-10V). Analog integrated temperature and humidity sensor can transform the changes in temperature and humidity into the changes in current/voltage values simultaneously, directly connect the secondary instruments with various standard analog inputs. HENGKO digital temperature and humidity control with soil moisture temperature probe, digital monitor display can show the temperature, humidity and dew point, realizing the control and monitor. Our sensor shell is waterproof, can prevent water from seeping into the sensor and damaging the sensor. It is widely used in HVAC, weather station, test and measurement, medical treatment, humidifier and other fields, especially suitable for acid, alkali, corrosion, high temperature and high pressure industrial harsh environment.
2. RS485 temperature and humidity sensor
Its circuit adopts a microprocessor chip and temperature sensor to ensure the reliability, stability and interchangeability of the product. The output is RS485, standard Modbus, which can monitor and control the computer system reliably. HENGKO RS485 temperature and humidity detector probe, cable series sensor with sintered metal filter housing have the advantage of larger permeability, high gas humidity flow and fast exchange rate. Our waterproof sensor housing keeps water from seeping into the body of the sensor and damaging it, widely used in agriculture, HVAC, weather station, test and measurement, medical, humidifier and other fields, especially suitable for acid, alkali, corrosion, high temperature and high pressure and another industrial harsh environment.
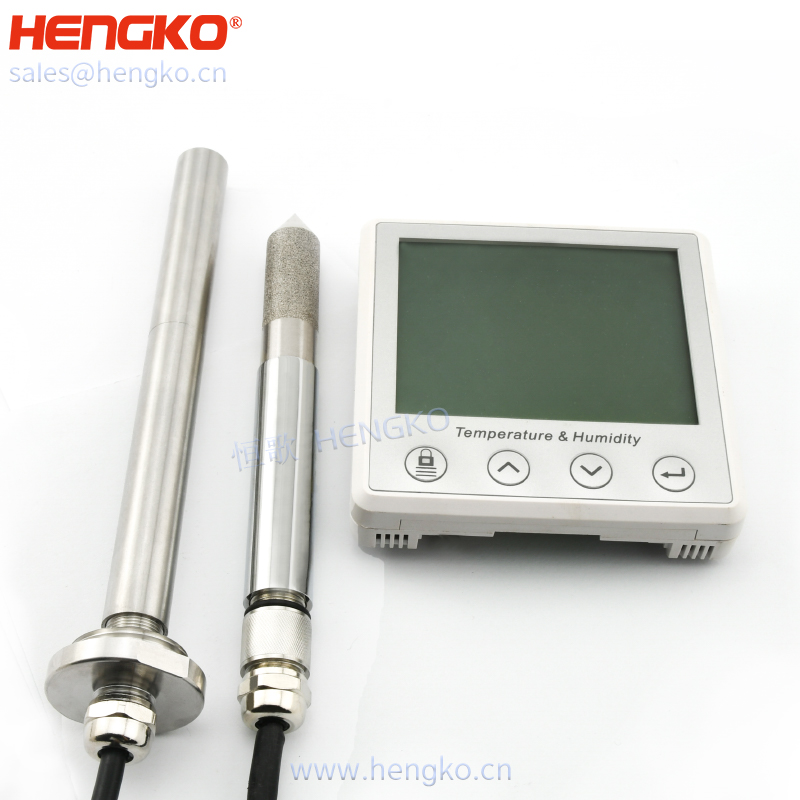

3. Network temperature and humidity sensor
Network temperature and humidity sensor can collect tem & humidity data and upload it to the server via ethernet、WiFi/GPRS.It makes full use of the communication network that has been set up to achieve long-distance data acquisition and transmission, to achieve the centralized monitoring of temperature and humidity data. This greatly reduced the construction, improve the efficiency of construction and maintenance costs.
Ethernet temperature and humidity transmitter collect temperature and humidity data and upload it to the server via ethernet. Wifi Temperature and humidity transmitter collect wifi. GPRS is the temperature and humidity transmitter base on the GPRS transfer. It just needs a SIM to upload the temperature and humidity data collected by the network base station. It is widely used in drug transport vehicles, industrial control, building control, electric power, measurement and testing, warehouse, cold storage and other industries.
HENGKO is the main supplier of the micro-sintered stainless steel filters and high-temperature porous metal filters in global. We have many kinds of sizes, specifications and types product for your choose, multiprocess and complicated filtering products also can be customized as your requirement.
What Different industrial humidity and temperature sensor and Room Humidity Sensor ?
As some people will think common temperature and humidity sensors is for home use or normal room sensor to use , then let check what the
difference both industrial humidity and temperature sensor and Room Humidity Sensor.
Industrial humidity and temperature sensors and room humidity sensors serve the same purpose of measuring environmental conditions,
but they are designed to cater to different applications and environments. Let's explore the differences between these two types of sensors:
1. Industrial Humidity and Temperature Sensors:
Industrial humidity and temperature sensors are specifically designed for harsh and demanding environments typically found in industrial settings. These sensors are built to withstand extreme temperatures, high levels of humidity, and exposure to various chemicals, dust, and contaminants. They are commonly used in industrial processes, manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and other industrial applications where precise and reliable measurements are crucial.
Characteristics of Industrial Humidity and Temperature Sensors:
* Robust Construction: Industrial sensors are often housed in rugged enclosures made of materials that can withstand physical stress, corrosion, and exposure to harsh substances.
* Wide Temperature Range: They can operate effectively in a wide temperature range, from very low to high temperatures, depending on the specific application requirements.
* High Accuracy: Industrial sensors are engineered for accuracy and stability in measuring both humidity and temperature to ensure the proper functioning of industrial processes.
* Scalability: These sensors may come with options for integration with industrial control systems and networks, allowing for remote monitoring and automation.
2. Room Humidity Sensor:
Room humidity sensors are designed for indoor environments, such as offices, homes, hospitals, and other commercial or residential spaces. Their main focus is on providing a comfortable and healthy living or working environment by monitoring and controlling indoor humidity levels.
Characteristics of Room Humidity Sensors:
* Aesthetic Design: Room sensors are often designed to be aesthetically pleasing and blend with the interior decor of a room or building.
* Moderate Environment Compatibility: They are optimized for indoor use and can handle typical room temperatures and humidity levels.
* Cost-Effectiveness: Room sensors are generally more cost-effective compared to industrial sensors since they don't require the same level of ruggedness and specialized features.
* User-Friendly Features: Many room humidity sensors come with user-friendly interfaces, such as displays or mobile apps, allowing occupants to monitor and adjust humidity levels easily.
While both types of sensors measure humidity and temperature, the key differences lie in their construction, durability, temperature range, accuracy, and the specific environments they are intended for. Industrial sensors are engineered to withstand harsh conditions and provide highly accurate measurements for industrial processes, while room sensors prioritize aesthetics, user-friendliness, and comfort for indoor environments.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a temperature sensor and a humidity sensor?
The main difference between a temperature sensor and a humidity sensor lies in the environmental parameter they measure:
Temperature Sensor:
A temperature sensor is a device designed to measure the degree of hotness or coldness of an object or the surrounding environment. It provides information about the temperature in terms of Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F) or sometimes in Kelvin (K) units. Temperature sensors are commonly used in various applications, including weather monitoring, climate control, industrial processes, electronic devices, and many others.
The fundamental principle behind temperature sensing involves detecting changes in physical properties of materials as they respond to temperature variations. Different types of temperature sensors, such as thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), thermistors, and infrared sensors, utilize distinct physical phenomena to convert temperature changes into electrical signals, which can then be measured and interpreted.
Humidity Sensor:
A humidity sensor, also known as a hygrometer, is a device used to measure the amount of moisture or water vapor present in the air or a gas. Humidity is commonly expressed as relative humidity (RH), representing the percentage of water vapor present relative to the maximum amount the air can hold at a specific temperature.
Humidity sensors are crucial in applications where controlling and monitoring humidity levels is essential for various reasons, such as maintaining comfort, preventing mold growth, ensuring proper storage conditions, and optimizing industrial processes.
Different types of humidity sensors exist, including capacitive, resistive, and thermal conductivity-based sensors. These sensors use distinct mechanisms to detect changes in moisture content and convert them into electrical signals, providing information about the humidity level.
In summary, the main difference between a temperature sensor and a humidity sensor is the environmental parameter they measure. Temperature sensors measure the degree of hotness or coldness in Celsius or Fahrenheit, while humidity sensors measure the moisture content in the air, typically expressed as relative humidity in percentage. Both sensors are vital in numerous applications, and their accurate measurements contribute to improved comfort, safety, and efficiency in various settings.
2. Are temperature and humidity sensors expensive?
The price varies depending on the type of sensor and its application. Some like thermocouples are quite affordable,
while others like certain types of RTDs can be costly.
3. Can I use a temperature and humidity sensor at home?
Absolutely! They are commonly used in home automation systems, including HVAC units and smart home devices.
4. Are these sensors hard to maintain?
Not really. Most sensors are designed for durability and require little to no maintenance. However,
regular calibration may be needed for optimal performance.
5. Do these sensors have any environmental impact?
No, these sensors are generally safe and do not have a negative environmental impact. Their purpose is to help
monitor and manage environmental conditions effectively.
Intrigued by the world of temperature and humidity sensors? Want to explore their capabilities further or perhaps implement them in your projects?
experts at HENGKO are ready to answer your queries and provide high-quality sensors for your needs. Contact them today
at ka@hengko.com to learn more about how these sensors can benefit you or your business. Don't hesitate - your environment could start
benefiting from this technology today!
Post time: Sep-05-2020